Test run using example data
An example set is provided with the UBCG2 package. Please follow the instruction below:
- Unzip the UBCG2 package. External programs (See requirements in the download page) must be installed and their path must be designated in the programPath file.
- Example fasta files are in the "fasta" directory. Execute the commands given here to convert fasta files to ucg files.
- Check the "ucg" directory by entering a command like "ls ucg/" where you will be able to find eight *.ucg files that contain UBCG gene sequences with metadata.
- Execute the following line in the directory where UBCGtree.jar file exists to align gene sequences and infer the UBCG tree.
- java -jar UBCGtree.jar align -ucg_dir ucg -run_id my_example -leaf label
- Outputs will be saved in the "output/my_example" directory
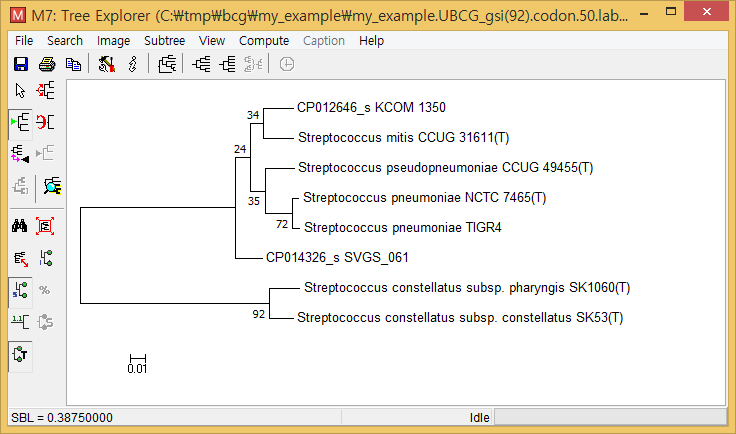
- Take the "concatenated_gsi(n).nwk" file and open with MEGA or other tree-viewing programs. (The below is the screenshot of MEGA.)
This UBCG tree shows that
- Two Streptococcus constellatus subspecies are closely related; all 92 UBCGs (Bacterial core gene set) supported this.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4 is closely related to the type strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae; 72 out of UBCGs supported this.
- Two tentatively new species, named CP012646_s and CP014326_s, formed a monophyletic clade with S. pneumoniae, Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae, and Streptococcus mitis.
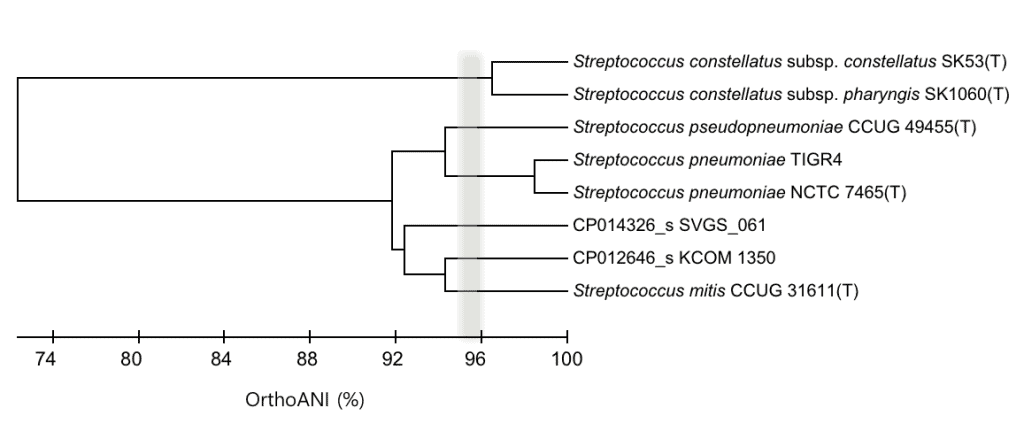
The below is the dendrogram showing OrthoANI-based clustering of the same genomes. Please note that CP012646_s and CP014326_s represent a novel species using 95~96% average nucleotide identity (ANI) cutoff [Learn more].